SPG11 Antibody
Catalog# : 5015
Hereditary spastic paraplegias (HSPs) are genetically and phenotypically heterogeneous disorders. Spastic paraplegia with thinning of the corpus callosum (ARHSP-TCC) is a relatively frequent form of complicated hereditary spastic paraplegia (cHSP) in which mental retardation and muscle stiffness at onset are followed by slowly progressive paraparesis and cognitive deterioration. Mutations of the SPG11 gene encoding the spatacsin protein have been identified as a major cause of HSP-TCC. Spatacsin is a potential transmembrane protein that is phosphorylated upon DNA damage. It is expressed in all structures of the brain, with a high expression in the cerebellum. SPG11 mutations may occur more frequently in familial than sporadic forms of cHSP without TCC. Kjellin syndrome is found to be associated with mutations in not only the SPG15 gene but also SPG11 gene. Recent studies show Parkinsonism may initiate SPG11-linked HSP TCC and that SPG11 may cause juvenile Parkinsonism.
Additional Names : SPG11, Spastic paraplegia 11, colorectal carcinoma-associated protein, spatacsin
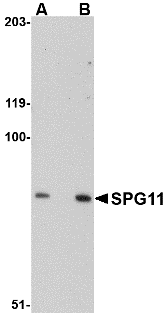 Description
Description
Left: Western blot analysis of SPG11 in mouse heart tissue lysate with SPG11 antibody at (A) 0.5 and (B) 1 µg/ml.
Source : SPG11 antibody was raised against a 15 amino acid peptide of human SPG11.
Purification : Affinity chromatography purified via peptide column
Clonality and Clone : This is a polyclonal antibody.
Host : SPG11 antibody was raised in rabbit. Please use anti-rabbit secondary antibodies.
Application : SPG11 antibody can be used for detection of SPG11 by Western blot at 0.5 – 1 µg/ml.
Tested Application(s) : E, WB
Buffer : Antibody is supplied in PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide.
Blocking Peptide : Cat.No. 5015P - SPG11 Peptide
Long-Term Storage : SPG11 antibody can be stored at 4ºC, stable for one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures.
Positive Control
1. Cat. No. 1401 - Mouse Heart Tissue Lysate
Species Reactivity :H, M, R
GI Number : 158253417
Accession Number : AAI53880
Short Description : Spastic paraplegia 15
References
1. Stevanin G, Azzedine H, Denora P, et al. Mutations in SPG11, encoding spatacsin, are a major cause of spastic paraplegia with thin corpus callosum. Nature Gen. 2007; 39:366–372.
2. Paisan-Ruiz C, Dogu O, Yilmaz A, et al. SPG11 mutations are common in familial cases of complicated hereditary spastic paraplegia. Neurology 2008; 70:1384-9.
3. Crimella C, Arnoldi A, Crippa F, et al. Point mutations and a large intragenic deletion in SPG11 in complicated spastic paraplegia without thin corpus callosum. J. Med. Genet. 2009; 46:345-51.
4. Orlén H, Melberg A, Raininko R, et al. SPG11 mutations cause Kjellin syndrome, a hereditary spastic paraplegia with thin corpus callosum and central retinal degeneration. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2009; epub.
SODD Antibody
Catalog# : 2143
Apoptosis is induced by certain cytokines including TNF and Fas ligand of the TNF family through their death domain containing receptors, TNF-R1 and Fas. Several novel death receptors including DR3, DR4, DR5, and DR6 were recently identified. Cell death signal is transduced by death domain containing adapter molecules through the interaction with death domain of these death receptors. A novel TNF-R1 interacting protein was recently identified and designated SODD for silencer of death domains (1). SODD associates with the death domain of TNF-R1 and prevents constitutive activation of TNF-R1 signaling. TNF treatment releases SODD and permits adapter molecules such as TRADD recruiting to the active TNF-R1 complex, which activates TNF signaling pathways. SODD also interacts with DR3. SODD is ubiquitously expressed in human tissues and cell lines.
Additional Names : SODD (NT), SODD
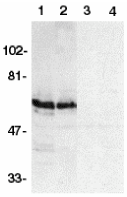 Description
Description
Left: Western blot analysis of SODD in HeLa (1,3) and THP-1 (2,4) whole cell lysates in the absence (1,2) or presence (3,4) of blocking peptide (Catalog no. 2143P) with SODD antibody at 1:500 dilution.
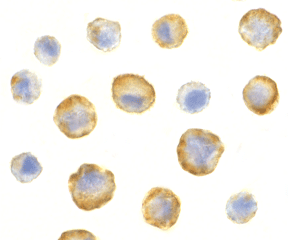
Below: Immunocytochemistry of SODD in HeLa cells with SODD antibody at 5 µg/ml.
Other Product Images
 Source : SODD antibody was raised against a peptide corresponding to amino acids near the amino terminus of human SODD.
Source : SODD antibody was raised against a peptide corresponding to amino acids near the amino terminus of human SODD.
Purification : Antibody is DEAE purified
Clonality and Clone : This is a polyclonal antibody.
Host : SODD antibody was raised in rabbit. Please use anti-rabbit secondary antibodies.
Immunogen : Human SODD (N-Terminus) Peptide (Cat. No. 2143P)
Application : SODD antibody can be used for detection of SODD by Western blot at 1:500 to 1:2000 dilution. An approximately 60 kDa band can be detected.
Tested Application(s) : E, WB, ICC
Buffer : Antibody is supplied in PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide.
Blocking Peptide : Cat. No. 2143P - SODD Peptide
Long-Term Storage : SODD antibody can be stored at 4ºC, stable for one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures.
Positive Control
1. Cat. No. 1201 - HeLa Cell Lysate
2. Cat. No. 1208 - THP-1 Whole Cell Lysate
Species Reactivity :H, M, R
GI Number : 4160013
Accession Number : AF111116
Short Description : (NT) Silencer Of Death Domains
References
1. Jiang Y, Woronicz JD, Liu W, Goeddel DY. Prevention of constitutive TNF receptor 1 signaling by silencer of death domains. Science 1999;283:543-6 (RD1299)
Smac Antibody
Catalog# : 2409
The inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAPs) regulate programmed cell death by inhibiting members of the caspase family of enzymes. A novel mammalian protein that binds to IAPs and neutralizes the inhibitory effect of IAPs on caspases was recently identified and designated Smac/DIABLO (1,2). Smac/DIABLO is a mitochondrial protein that is released along with cytochrome c during apoptosis and activates cytochrome c/Apaf-1/capase-9 pathway. Analysis of the structural basis of Smac/DIABLO reveals that the N-terminal amino acids are required for binding of Smac/DIABLO to IAPs and activation of caspases (3-6). Smac/DIABLO is expressed in a variety of human and mouse tissues (1,2).
Additional Names : Smac (CT), DIABLO
 Description
Description
Left: Western blot analysis of Smac in human heart tissue lysate in the absence (A) or presence (B) of blocking peptide (2409P) with Smac antibody at 1 µg /ml.
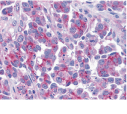
Below: Immunohistochemistry of Smac/DIABLO in human ovary tissue with Smac antibody at 5 µg/ml.
Other Product Images
 Source : Smac antibody was raised against a peptide corresponding to amino acids 225 to 239 of human Smac/DIABLO .
Source : Smac antibody was raised against a peptide corresponding to amino acids 225 to 239 of human Smac/DIABLO .
Purification : Affinity chromatography purified via peptide column
Clonality and Clone : This is a polyclonal antibody.
Host : Smac antibody was raised in rabbit. Please use anti-rabbit secondary antibodies.
Immunogen : Human Smac / DIABLO (C-Terminus) Peptide (Cat. No. 2409P)
Application : Smac antibody can be used for detection of Smac/DIABLO by Western blot at 0.5 to 1 µg/ml.Human heart tissue lysate can be used as positive control and a 25 kDa band can be detected.
Tested Application(s) : E, WB, IHC
Buffer : Antibody is supplied in PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide.
Blocking Peptide : Cat. No. 2409P - Smac Peptide
Long-Term Storage : Smac antibody can be stored at 4ºC, stable for one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures.
Positive Control
1. Cat. No. 1301 - Human Heart Tissue Lysate
2. Cat. No. 1316 - Human Ovary Tissue Lysate
Species Reactivity :H, M, R
GI Number : 9454219
Accession Number : AAF87716
Short Description : (CT) IAPs binding protein
References
1. Du C, Fang M, Li Y, Li L, Wang X. Smac, a mitochondrial protein that promotes cytochrome c-dependent caspase activation by eliminating IAP inhibition. M Cell. 2000;102(1):33-42.
2. Verhagen AM, Ekert PG, Pakusch M, Silke J, Connolly LM, Reid GE, Moritz RL, Simpson RJ, Vaux DL. Identification of DIABLO, a mammalian protein that promotes apoptosis by binding to and antagonizing IAP proteins. Cell. 2000;102(1):43-53.
3. Srinivasula SM, Datta P, Fan XJ, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Huang Z, Alnemri ES. Molecular Determinants of the Caspase-promoting Activity of Smac/DIABLO and Its Role in the Death Receptor Pathway. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(46):36152-36157.
4. Chai J, Du C, Wu JW, Kyin S, Wang X, Shi Y. Structural and biochemical basis of apoptotic activation by Smac/DIABLO. Nature. 2000;406(6798):855-62.
Smac Antibody
Catalog# : 2411
The inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAPs) regulate programmed cell death by inhibiting members of the caspase family of enzymes. A novel mammalian protein that binds to IAPs and neutralizes the inhibitory effect of IAPs on caspases was recently identified and designated Smac/DIABLO (1,2). Smac/DIABLO is a mitochondrial protein that is released along with cytochrome c during apoptosis and activates cytochrome c/Apaf-1/capase-9 pathway. Analysis of the structural basis of Smac/DIABLO reveals that the N-terminal amino acids are required for binding of Smac/DIABLO to IAPs and activation of caspases (3-6). Smac/DIABLO is expressed in a variety of human and mouse tissues (1,2).
Additional Names : Smac (CT), DIABLO, mSmac
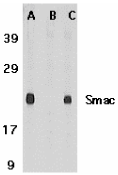 Description
Description
Left: Western blot analysis of Smac in mouse heart tissue lysate in the absence (A) or presence (B) of blocking and in rat heart tissue lysate with Smac peptide antibody at 1 µg /ml.
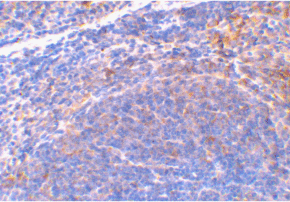
Below: Immunohistochemical staining of mouse spleen tissue using Smac antibody at 2 µg/ml.
Other Product Images
 Source : Smac antibody was raised against a peptide corresponding to amino acids 222 to 237 of murine Smac/DIABLO.
Source : Smac antibody was raised against a peptide corresponding to amino acids 222 to 237 of murine Smac/DIABLO.
Purification : Affinity chromatography purified via peptide column
Clonality and Clone : This is a polyclonal antibody.
Host : Smac antibody was raised in rabbit. Please use anti-rabbit secondary antibodies.
Immunogen : Human Smac Peptide (Cat. No. 2411P)
Application : Smac antibody can be used for detection of Smac by Western blot at 0.5 to 1 µg/ml.A 25 kDa band can be detected.
Tested Application(s) : E, WB, IHC
Buffer : Antibody is supplied in PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide.
Blocking Peptide : Cat. No. 2411P - Smac Peptide
Long-Term Storage : Smac antibody can be stored at 4ºC, stable for one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures.
Positive Control
1. Cat. No. 1401 - Mouse Heart Tissue Lysate
Species Reactivity :H, M, R
GI Number : 8953908
Accession Number : AF203914
Short Description : (CT) IAPs binding protein
References
1. Du C, Fang M, Li Y, Li L, Wang X. Smac, a mitochondrial protein that promotes cytochrome c-dependent caspase activation by eliminating IAP inhibition. Cell. 2000;102(1):33-42.
2. Verhagen AM, Ekert PG, Pakusch M, Silke J, Connolly LM, Reid GE, Moritz RL, Simpson RJ, Vaux DL. Identification of DIABLO, a mammalian protein that promotes apoptosis by binding to and antagonizing IAP proteins. Cell. 2000;102(1):43-53.
3. Srinivasula SM, Datta P, Fan XJ, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Huang Z, Alnemri ES. Molecular Determinants of the Caspase-promoting Activity of Smac/DIABLO and Its Role in the Death Receptor Pathway. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(46):36152-36157.
4. Chai J, Du C, Wu JW, Kyin S, Wang X, Shi Y. Structural and biochemical basis of apoptotic activation by Smac/DIABLO. Nature. 2000;406(6798):855-62.
Rkhd4 Antibody
Catalog# : 4869
Rkhd4, also known as MEX3A is a member of a novel family of four homologous human MEX3 proteins each containing two heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K homology (KH) domains and one carboxy-terminal RING finger module. MEX3 proteins, including Rkhd4, are phosphoproteins that bind RNA through their KH domains and shuttle between the nucleus and the cytoplasm via the CRM1 export pathway. These proteins are a novel family of evolutionarily conserved RNA-binding proteins, differentially recruited to P bodies and potentially involved in post-transcriptional regulatory mechanisms. While Rkhd2 has been suggested to be associated with susceptibility to essential hypertension type 8, the function of Rkhd4 remains unknown. Rkhd3 and Rkhd4, but not Rkhd2, co-localize with both the hDcp1a decapping factor and Argonaute (Ago) proteins in processing bodies (P bodies), recently characterized as centers of mRNA turnover.
Additional Names : Rkhd4, MEX3A, MEX3-A
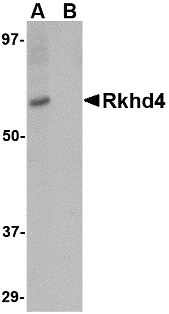 Description
Description
Left: Western blot analysis of Rkhd4 in SK-N-SH cell lysate with Rkhd4 antibody at 1 µg/ml in (A) the absence and (B) the presence of blocking peptide.
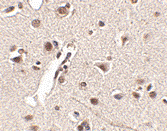
Below: Immunohistochemistry of Rkhd4 in human brain tissue with Rkhd4 antibody at 2.5 µg/ml.
Other Product Images
 Source : Rkhd4 antibody was raised against a 14 amino acid peptide from near the carboxy terminus of human Rkhd4.
Source : Rkhd4 antibody was raised against a 14 amino acid peptide from near the carboxy terminus of human Rkhd4.
Purification : Affinity chromatography purified via peptide column
Clonality and Clone : This is a polyclonal antibody.
Host : Rkhd4 antibody was raised in rabbit. Please use anti-rabbit secondary antibodies.
Application : Rkhd4 antibody can be used for detection of Rkhd4 by Western blot at 1 - 2 µg/ml.
Tested Application(s) : E, WB, IHC
Buffer : Antibody is supplied in PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide.
Blocking Peptide : Cat.No. 4869P - Rkhd4 Peptide
Long-Term Storage : Rkhd4 antibody can be stored at 4ºC, stable for one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures.
Positive Control
1. Cat. No. 1220 - SK-N-SH Cell Lysate
Species Reactivity :H, M, R
GI Number : 134034168
Accession Number : A1L020
Short Description : RNA binding, Bcl-2, apoptosis, Mex3, decapping
References
1. Draper BW, Mello CC, Bowerman B, et al. MEX-3 is a KH domain protein that regulates blastomere identity in early C. elegans embryos. Cell 1996; 87:205–16.
2. Liu J, Valencia-Sanchez MA, Hannon GJ, et al. MicroRNA-dependent localization of targeted mRNAs to mammalian P-bodies. Nat. Cell Biol 2005; 7:719–23.
3. Guzman B, Cormand B, Ribases M, et al. Implication of chromosome 18 in hypertension by sibling pair and association analyses: putative involvement of the RKHD2 gene. Hypertension 2006; 48:883-91.
4. Buchet-Poyau K, Courchet J, Le Hir H, et al. Identification and characterization of human Mex-3 proteins, a novel family of evolutionarily conserved RNA-binding proteins differentially localized to processing bodies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007; 35:1289-300.
Bio Synthesis may use your oligosaccharides for preparation of the conjugates or in some cases it could prepare the whole conjugate, including the oligosaccharide moiety. For the preparation of oligopeptides and oligonucleotides glycoconjugates these compounds are modified during solid phase synthesis to introduce a spacer carrying a functional group that can be used for subsequent cross-linking with the oligosaccharides. Depending on the nature of the oligosaccharide and the peptide or oligonucleotide the length and hydrophilicity of the spacer would be decided to maximize the interactions of these compounds with their receptors.
Glycoconjugates
Advances in glycobiology highlight the role of naturally occurring glycoconjugates in different biological processes. The most common glycoconjugates are those where an oligosaccharide is covalently linked to a protein, peptide or lipid, yet in some cases it can be also linked to an oligonucleotide. Synthetic conjugates are excellent tools to elucidate the natural glycoconjugates' roles in different biological processes. In these conjugates an oligosaccharide is usually cross-linked to a reporter group, such as a fluorochrome, enzyme, liposome, colloidal gold and others, that can be easily detected.
Other Useful Tools
Other useful tools in biological studies are those compounds where the oligosaccharide is coupled to a fluorescent label such as fluorescein, rhodamine, Texas red and others, either directly or via a spacer. Fluorescent compounds can be detected by fluorescence microscopy, FACS machine, and spectrofluorometry. Other tagging methods involve the use of colloidal gold and ferritin, both compounds that can be detected by electron microscopy. Oligosaccharides can also be conjugated to different lipids to yield glycolipids that can be incorporated into either micelles or liposomes, with the latter being effective drug carriers.
Glycoconjugates of Oligosaccharides
The same methods used to prepare glycoconjugates of oligosaccharides can be applied to native polysaccharides. Base on the needs for sensitivity, nature of the molecule recognizing the sugar moiety, Bio-Synthesis can design a method to label these macromolecules without interfering with their interactions with other molecules.
Toxin
Bio Synthesis extensive experience in peptide and oligonucleotide synthesis coupled to its work over the past years in the glycosides area would allow its staff to design the best compound to satisfy your needs as well as its effective preparation.
Toxin Conjugates
These conjugates consist of one of the several naturally occurring toxic peptides or proteins, e.g. ricin, cholera toxin and cone snail neurotoxin, cross-linked to a ligand, e.g. peptide, protein, oligonucleotide, oligosaccharide or their analogs, that specifically bind to certain cell receptors. Thus, the role of the ligand is to largely target the delivery of the toxin to those cells that express a specific receptor, while that of the toxin moiety is to interact with specific enzymes or cellular receptors and interfere with their normal functions.
Conjugation of Toxins with Peptide Ligands
Toxins can be conjugated to peptide ligands, such as peptide hormones, (somatostatin and bombesin), tumor-homing peptides or to proteins via a spacer which can have a disulfide bond that can be cleaved by reducing agents. The flexibility of the spacer can affect the toxin performance having a higher activity when linked by more flexible spacers. In some cases the toxins can be linked to certain antigen-specific antibodies to yield immunotoxins that are conjugates with significant potential in cancer therapy.
Conjugation of Toxins with Oligonucleotides
In this case, the toxin is conjugated to an ODN sequence called an aptamer. Aptamers, like antibodies, can provide specific molecular recognition that is useful for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. The methodology used to produce toxin-aptamer conjugates is in several aspects similar to that used to produce ODN-peptide conjugates.
Conjugation of Toxins with Oligosaccharides
Another family of compounds to which toxins can be conjugated is oligosaccharides. At the present the main application of oligosaccharide-toxin conjugates is the vaccine area to elicit an immune response against the oligosaccharide moiety of the conjugate. Different from peptide and oligonucleotide conjugates and in order to stimulate the correct immune response the structural requirements for linking of the oligosaccharide to the toxin are more stringent. Thus, this type of conjugations would require chemical procedures designed to satisfy those structural requirements.
Rkhd2 Antibody
Catalog# : 4857
Rkhd2, also known as MEX3C is a member of a novel family of four homologous human MEX3 proteins each containing two heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K homology (KH) domains and one carboxy-terminal RING finger module. MEX3 proteins, including Rkhd2, are phosphoproteins that bind RNA through their KH domains and shuttle between the nucleus and the cytoplasm via the CRM1 export pathway. These proteins are a novel family of evolutionarily conserved RNA-binding proteins, differentially recruited to P bodies and potentially involved in post-transcriptional regulatory mechanisms. It has been suggested that genetic variations in Rkhd2 may be associated with susceptibility to essential hypertension type 8. Rkhd3 and Rkhd4, but not Rkhd2, co-localize with both the hDcp1a decapping factor and Argonaute (Ago) proteins in processing bodies (P bodies), recently characterized as centers of mRNA turnover.
Additional Names : Rkhd2, RING finger and KH domain-containing protein 2, RING finger protein 194, MEX3C, RNF194
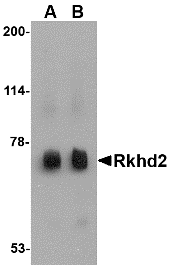 Description
Description
Left: Western blot analysis of Rkhd2 in rat heart tissue lysate with Rkhd2 antibody at (A) 0.5 µg/ml and (B) 1 µg/ml.
Source : Rkhd2 antibody was raised against a 15 amino acid peptide from near the carboxy terminus of human RKHD2.
Purification : Affinity chromatography purified via peptide column
Clonality and Clone : This is a polyclonal antibody.
Host : Rkhd2 antibody was raised in rabbit. Please use anti-rabbit secondary antibodies.
Application : Rkhd2 antibody can be used for detection of Rkhd2 by Western blot at 0.5 – 1 µg/ml.
Tested Application(s) : E, WB
Buffer : Antibody is supplied in PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide.
Blocking Peptide : Cat.No. 4857P - Rkhd2 Peptide
Long-Term Storage : Rkhd2 antibody can be stored at 4ºC, stable for one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures.
Positive Control
1. Cat. No. 1461 - Rat Heart Tissue Lysate
Species Reactivity :H, M, R
GI Number : 148229134
Accession Number : NP_057710
Short Description : RING finger and KH domain-containing protein 2
References
1. Draper BW, Mello CC, Bowerman B, et al. MEX-3 is a KH domain protein that regulates blastomere identity in early C. elegans embryos. Cell 1996; 87:205–16.
2. Liu J, Valencia-Sanchez MA, Hannon GJ, et al. MicroRNA-dependent localization of targeted mRNAs to mammalian P-bodies. Nat. Cell Biol 2005; 7:719–23.
3. Guzman B, Cormand B, Ribases M, et al. Implication of chromosome 18 in hypertension by sibling pair and association analyses: putative involvement of the RKHD2 gene. Hypertension 2006; 48:883-91.
4. Buchet-Poyau K, Courchet J, Le Hir H, et al. Identification and characterization of human Mex-3 proteins, a novel family of evolutionarily conserved RNA-binding proteins differentially localized to processing bodies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007; 35:1289-300.
Rkhd1 Antibody
Catalog# : 4835
Rkhd1, also known as TINO or MEX3D is a member of a novel family of four homologous human MEX3 proteins each containing two heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K homology (KH) domains and one carboxy-terminal RING finger module. MEX3 proteins, including Rkhd1, are phosphoproteins that bind RNA through their KH domains and shuttle between the nucleus and the cytoplasm via the CRM1 export pathway. These proteins are a novel family of evolutionarily conserved RNA-binding proteins, differentially recruited to P bodies and potentially involved in post-transcriptional regulatory mechanisms. Rkhd1 binds to the AU-rich element in the 3’-untranslated region of Bcl-2 mRNA and is thought to be a negative regulator of Bcl-2 expression. Rkhd3 and Rkhd4, but not Rkhd1, co-localize with both the hDcp1a decapping factor and Argonaute (Ago) proteins in processing bodies (P bodies), recently characterized as centers of mRNA turnover.
Additional Names : Rkhd1, RING finger and KH domain-containing protein 1, MEX3D, TINO, RING finger protein 193, RNF193
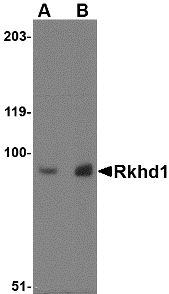 Description
Description
Left: Western blot analysis of Rkhd1 in MDA-MB-361 cell lysate with Rkhd1 antibody at (A) 1 µg/ml and (B) 2 µg/ml.
Below: Immunohistochemistry of Rkhd1 in human small intestine tissue with Rkhd1 antibody at 2.5 µg/ml.
Other Product Images
 Source : Rkhd1 antibody was raised against a 15 amino acid peptide from near the center of human Rkhd1.
Source : Rkhd1 antibody was raised against a 15 amino acid peptide from near the center of human Rkhd1.
Purification : Affinity chromatography purified via peptide column
Clonality and Clone : This is a polyclonal antibody.
Host : Rkhd1 antibody was raised in rabbit. Please use anti-rabbit secondary antibodies.
Application : Rkhd1 antibody can be used for detection of Rkhd1 by Western blot at 1 – 2 µg/ml.
Tested Application(s) : E, WB, IHC
Buffer : Antibody is supplied in PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide.
Blocking Peptide : Cat.No. 4835P - Rkhd1 Peptide
Long-Term Storage : Rkhd1 antibody can be stored at 4ºC, stable for one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures.
Positive Control
1. Cat. No. 1217 - MDA-MB-361 Cell Lysate
Species Reactivity :H
GI Number : 134047829
Accession Number : Q86XN8
Short Description : RING finger and KH domain-containing protein 1
References
1. Donnini M, Lapucci A, Papucci L, et al. Identification of TINO: A new evolutionarily conserved Bcl-2 AU-rich element RNA-binding protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2004; 279:20154-66.
2. Draper BW, Mello CC, Bowerman B, et al. MEX-3 is a KH domain protein that regulates blastomere identity in early C. elegans embryos. Cell 1996; 87:205–16.
3. Liu J, Valencia-Sanchez MA, Hannon GJ, et al. MicroRNA-dependent localization of targeted mRNAs to mammalian P-bodies. Nat. Cell Biol 2005; 7:719–23.
4. Buchet-Poyau K, Courchet J, Le Hir H, et al. Identification and characterization of human Mex-3 proteins, a novel family of evolutionarily conserved RNA-binding proteins differentially localized to processing bodies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007; 35:1289-300.
RIPK1 Antibody
Catalog# : 5389
RIPK1 (Receptor Interacting Protein) is a crucial 74 kD adaptor kinase in several of stress-induced signaling pathways and on the crossroad of a cell’s decision to live or die. RIPK1 contains an N-terminal region with homology to protein kinases, an intermediate domain capable of association with MAPKKK and a C-terminal region containing a death domain motif present in the Fas and TNFR1 intracellular domains. Full length RIPK1 is important for signallling to NF-kappa-B, MAPKs and necrosis, whereas caspase-8 generates a C-terminal RIPK1 cleavage fragment, promoting TNF-induced apoptosis. It is required for TNFRSF1A-mediated and TLR3-induced NF-kappa-B activation. RIPK1-deficient mice fail to thrive, displaying extensive apoptosis in both lymphoid and adipose tissues and dying at 1-3 days of age.
Additional Names : RIPK1, Receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 1, RIP, RIP1
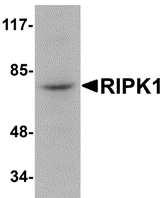
Description
Left: Western blot analysis of RIPK1 in rat kidney tissue lysate with RIPK1 antibody at 1 µg/ml.
Source : RIPK1 antibody was raised against a 15 amino acid peptide from near the amino terminus of human RIPK1.
Purification : Affinity chromatography purified via peptide column
Clonality and Clone : Polyclonal
Host : RIPK1 antibody was raised in rabbit. Please use anti-rabbit secondary antibodies.
Application : RIPK1 antibody can be used for detection of RIPK1 by Western blot at 1 - 2 µg/ml.
Tested Application(s) : E, WB
Buffer : Antibody is supplied in PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide.
Blocking Peptide : Cat.No. 5389P - RIPK1 Peptide
Long-Term Storage : RIPK1 antibody can be stored at 4ºC, stable for one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures.
Positive Control
1. Cat. No. 1465 - Rat Kidney Tissue Lysate
Species Reactivity :H, M, R
GI Number : 57242761
Accession Number : NP_003795
Short Description : Receptor-interacting kinase 1
References
1. Stanger BZ, Leder P, Lee TH, et al. RIP: a novel protein containing a death domain that interacts with Fas/APO-1 (CD95) in yeast and causes cell death. Cell 1995; 81:513-23.
2. Hsu H, Huang J, Shu HB, et al. TNF-dependent recruitment of the protein kinase RIP to the TNF receptor-1 signaling complex. Immunity 1996; 4:387-96.
3. Meylan E, Burns K, Hofmann K, et al. RIP1 is an essential mediator of Toll-like receptor 3-induced NF-kappa B activation. Nat. Immunol. 2004; 5:503-7.
4. Festjens N, Vanden Bergh T, Cornelis S, et al. RIP1, a kinase on the crossroads of a cell's decision to live or die. Cell Death Differ. 2007;14:400-10.
RIP3 Antibody
Catalog# : 2283
Certain serine/threonine protein kinases, such as ASK1, RIP, DAP, and ZIP kinases, are mediators of apoptosis. Receptor interacting proteins including RIP and RIP2/RICK mediate apoptosis induced by TNFR1 and Fas, two prototype members in the death receptor family. A novel member in the RIP kinase family was recently identified and designated RIP3 (1-3). RIP3 contains N-terminal kinase domain but, unlike RIP or RIP2, lacks the C-terminal death or CARD domain. RIP3 binds to RIP and TNFR1, mediates TNFR1 induced apoptosis, and attenuates RIP and TNFR1 induced NF-kB activation. Overexpression of RIP3 induces apoptosis and NF-kappaB activation. The messenger RNA of RIP3 is expressed in a subset of adult tissues (2,3).
Additional Names : RIP3
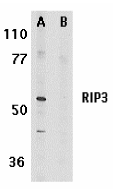 Description
Description
Left: Western blot analysis of RIP3 in mouse 3T3 whole cell lysate in the absence (A) or presence (B) of blocking peptide with RIP3 antibody at 1 µg/ml.
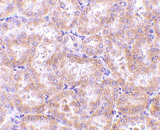
Below: Immunohistochemistry of RIP3 in rat kidney tissue with RIP3 antibody at 5 µg/ml.
Other Product Images
 Source : RIP3 antibody was raised against a peptide corresponding to amino acids 473 to 486 of murine RIP3.
Source : RIP3 antibody was raised against a peptide corresponding to amino acids 473 to 486 of murine RIP3.
Purification : Affinity chromatography purified via peptide column
Clonality and Clone : This is a polyclonal antibody.
Host : RIP3 antibody was raised in rabbit. Please use anti-rabbit secondary antibodies.
Immunogen : Human RIP3 Peptide (Cat. No. 2283P)
Application : RIP3 antibody can be used for detection of RIP3 by Western blot at 0.5 to 1 µg/ml.An approximately 57 kDa band can be detected.
Tested Application(s) : E, WB, IHC
Buffer : Antibody is supplied in PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide.
Blocking Peptide : Cat. No. 2283P - RIP3 Peptide
Long-Term Storage : RIP3 antibody can be stored at 4ºC, stable for one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures.
Positive Control
1. Cat. No. 1212 - 3T3 Cell Lysate
Species Reactivity :M, R
GI Number : 6063101
Accession Number : AAF03133
Short Description : Mouse Receptor Interacting Protein 3
References
1. Yu PW, Huang BC, Shen M, Quast J, Chan E, Xu X, Nolan GP, Payan DG, Luo Y. Identification of RIP3, a RIP-like kinase that activates apoptosis and NFkappaB. Curr Biol. 1999;9(10):539-42.
2. Sun X, Lee J, Navas T, Baldwin DT, Stewart TA, Dixit VM. RIP3, a novel apoptosis-inducing kinase. J Biol Chem. 1999;274(24):16871-5.
3. Pazdernik NJ, Donner DB, Goebl MG, Harrington MA. Mouse receptor interacting protein 3 does not contain a caspase-recruiting or a death domain but induces apoptosis and activates NF-kappaB. Mol Cell Bio. 1999; 19(10):6500-8 (WD0102)
RICK Antibody
Catalog# : 2075
Apoptosis is mediated by death domain (DD) and/or caspase recruitment domain (CARD) containing molecules and a caspase family of proteases. DD-containing serine/threonine kinase RIP regulates Fas-induced apoptosis. A novel CARD-containing serine/threonine kinase was recently identified and designated RICK/RIP2/CARDIAK for RIP-like interacting CLARP kinase, receptor interacting protein-2, and CARD-containing ICE associated kinase, respectively, (1-3). RICK contains an N-terminal kinase catalytic domain and a C-terminal CARD domain. Overexpression of RICK induced apoptosis and activation of NF-kappaB and JNK. RICK interacts with members of the TRAF family, CLARP and caspase-1. Thus, RICK represents a novel kinase that regulates TNF and Fas induced-apoptosis and that is involved in the generation of proinflammatory cytokine IL-1b. The messenger RNA of RICK is expressed in multiple human tissues.
Additional Names : RICK (NT), RIP2
 Description
Description
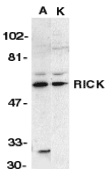
Left: Western blot analysis of RICK in A431 (A) and K562 (K) whole cell lysate with RICK antibody at 1:1000 dilution.
Below: Immunocytochemistry of RICK in A431 cells with RICK antibody at 10 µg/ml.
Other Product Images
 Source : RICK antibody was raised against a peptide corresponding to amino acids near the amino terminus of human RICK.
Source : RICK antibody was raised against a peptide corresponding to amino acids near the amino terminus of human RICK.
Purification : Affinity chromatography purified via peptide column
Clonality and Clone : This is a polyclonal antibody.
Host : RICK antibody was raised in rabbit. Please use anti-rabbit secondary antibodies.
Immunogen : Human RICK (N-Terminus) Peptide (Cat. No. 2075P)
Application : RICK antibody can be used for detection of RICK by Western blot at 1:1000 dilution. An approximately 60 kDa band can be detected.
Tested Application(s) : E, WB, ICC
Buffer : Antibody is supplied in PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide.
Blocking Peptide : Cat. No. 2075P - RICK Peptide
Long-Term Storage : RICK antibody can be stored at 4ºC, stable for one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures.
Positive Control
1. Cat. No. 1202 - A431 Cell Lysate
2. Cat. No. 1204 - K562 Cell Lysate
Species Reactivity :H, M, R
GI Number : 20455217
Accession Number : O43353
Short Description : (NT) RIP-like Interacting CLARP Kinase
References
1. Inohara N, del Peso L, Koseki T, Chen S, Nunez G. RICK, a novel protein kinase containing a caspase recruitment domain, interacts with CLARP and regulates CD95-mediated apoptosis. J Biol Chem 1998;273:12296-300
2. McCarthy JV, Ni J, Dixit VM. RIP2 is a novel NF-kappaB-activating and cell death-inducing kinase. J Biol Chem 1998;273:16968-75
3. Thome M, Hofmann K, Burns K, Martinon F, Bodmer JL, Mattmann C, Tschopp J. Identification of CARDIAK, a RIP-like kinase that associates with caspase-1. Curr Biol 1998;8:885-8 (RD1299)
RICK Antibody
Catalog# : 2183
Apoptosis is mediated by death domain (DD) and/or caspase recruitment domain (CARD) containing molecules and a caspase family of proteases. DD-containing serine/threonine kinase RIP regulates Fas-induced apoptosis. A novel CARD-containing serine/threonine kinase was recently identified and designated RICK/RIP2/CARDIAK for RIP-like interacting CLARP kinase, receptor interacting protein-2, and CARD-containing ICE associated kinase, respectively, (1-3). RICK contains an N-terminal kinase catalytic domain and a C-terminal CARD domain. Overexpression of RICK induced apoptosis and activation of NF-kappaB and JNK. RICK interacts with members of the TRAF family, CLARP and caspase-1. Thus, RICK represents a novel kinase that regulates TNF and Fas induced-apoptosis and that is involved in the generation of proinflammatory cytokine IL-1b. The messenger RNA of RICK is expressed in multiple human tissues (1).
Additional Names : RICK (CT), RIP2
Source : RICK antibody was raised against a peptide corresponding to amino acids 508 to 522 of human origin .
Purification : Affinity chromatography purified via peptide column
Clonality and Clone : This is a polyclonal antibody.
Host : RICK antibody was raised in rabbit. Please use anti-rabbit secondary antibodies.
Immunogen : Human RICK (C-Terminus) Peptide (Cat. No. 2183P)
Application : RICK antibody can be used for detection of RICK by Western blot at 1:500 dilution. An approximately 60 kDa band can be detected. It is human, mouse, and rat reactive.
Tested Application(s) : E, WB, ICC
Buffer : Antibody is supplied in PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide.
Blocking Peptide : Cat. No. 2183P - RICK Peptide
Long-Term Storage : RICK antibody can be stored at 4ºC, stable for one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures.
Positive Control
1. Cat. No. 1204 - K562 Cell Lysate
2. Cat. No. 1212 - 3T3 Whole Cell Lysate
Species Reactivity :H
GI Number : 3123886
Accession Number : AF027706
Short Description : (CT) RIP-like Interacting CLARP Kinase
References
1. Inohara N, del Peso L, Koseki T, Chen S, Nunez G. RICK, a novel protein kinase containing a caspase recruitment domain, interacts with CLARP and regulates CD95-mediated apoptosis. J Biol Chem 1998;273:12296-300
2. McCarthy JV, Ni J, Dixit VM. RIP2 is a novel NF-kappaB-activating and cell death-inducing kinase. J Biol Chem 1998;273:16968-75
3. Thome M, Hofmann K, Burns K, Martinon F, Bodmer JL, Mattmann C, Tschopp J. Identification of CARDIAK, a RIP-like kinase that associates with caspase-1. Curr Biol 1998;8:885-8 (WD0300)
RAIDD Antibody
Catalog# : 1117
Apoptosis, or programmed cell death, occurs during normal cellular differentiation and development of multicellular organisms. Apoptosis is induced by certain cytokines including TNF and Fas ligand of the TNF family through their death domain (DD)-containing receptors, TNFR1 and Fas. The death signals are transduced by a group of DD-containing adapter molecules. A novel cell death adapter was recently identified by two independent groups and designated RAIDD (RIP-associated ICH-1/CED-3-homologous protein with DD) and CRADD (caspase and RIP adapter with DD)1,RAIDD contains a DD and a CARD (for caspase recruitment domain) which interact with RIP and caspase, respectively, to transduce death signals. RAIDD is constitutively expressed in many tissues and mediates apoptosis caused by Fas and TNFR-1.
Additional Names : RAIDD (CT), CRADD
 Description
Description
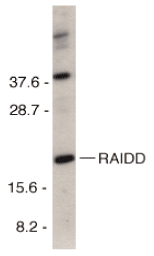
Left: Western blot analysis of RAIDD in HeLa total cell lysate with RAIDD antibody at 1 µg/ml.
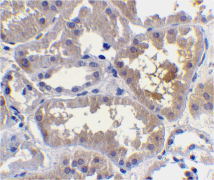
Below: Immunohistochemistry of RAIDD in human kidney tissue with RAIDD antibody at 10 µg/ml.
Other Product Images
 Source : RAIDD antibody was raised against a peptide corresponding to amino acids near the carboxy terminus of human RAIDD .
Source : RAIDD antibody was raised against a peptide corresponding to amino acids near the carboxy terminus of human RAIDD .
Purification : Antibody is DEAE purified
Clonality and Clone : This is a polyclonal antibody.
Host : RAIDD antibody was raised in rabbit. Please use anti-rabbit secondary antibodies.
Immunogen : Human RAIDD (C-Terminus) Peptide (Cat. No. 1117P)
Application : RAIDD antibody can be used for detection of RAIDD by Western blot at 1:500 to 1:1000 dilution. A 22 kDa band should be detected.
Tested Application(s) : E, WB, IHC
Buffer : Antibody is supplied in PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide.
Blocking Peptide : Cat. No. 1117P - RAIDD Peptide
Long-Term Storage : RAIDD antibody can be stored at 4ºC, stable for one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures.
Positive Control
1. Cat. No. 1201 - HeLa Cell Lysate
2. Cat. No. 1305 - Human Kidney Tissue Lysate
Species Reactivity :H
GI Number : 1785557
Accession Number : AAB42217
Short Description : (CT) Adapter Molecule
References
1. Duan H, Dixit VM. RAIDD is a new 'death' adaptor molecule. Nature 1997;385:86-89
2. Ahmad M, Srinivasula SM, Wang L, Talanian RV, Litwack G, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Alnemri ES. CRADD, a novel human apoptotic adaptor molecule for caspase-2, and FasL/tumor necrosis factor receptor-interacting protein RIP. Cancer Res 1997 57:615-619
3. Hofmann K, Bucher P, Tschopp J. The CARD domain: a new apoptotic signalling motif. Trends Biochem Sci 1997;22:155-156 (RD1299)
RAIDD Antibody
Catalog# : 1115
Apoptosis, or programmed cell death, occurs during normal cellular differentiation and development of multicellular organisms. Apoptosis is induced by certain cytokines including TNF and Fas ligand of the TNF family through their death domain (DD)-containing receptors, TNFR1 and Fas. The death signals are transduced by a group of DD-containing adapter molecules. A novel cell death adapter was recently identified by two independent groups and designated RAIDD (RIP-associated ICH-1/CED-3-homologous protein with DD) and CRADD (caspase and RIP adapter with DD)1,RAIDD contains a DD and a CARD (for caspase recruitment domain) which interact with RIP and caspase, respectively, to transduce death signals1,3. RAIDD is constitutively expressed in many tissues and mediates apoptosis caused by Fas and TNFR-1.
Additional Names : RAIDD (IN), CRADD
 Description
Description
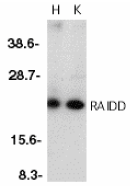
Left: Western blot analysis of RAIDD in whole cell lysates from HeLa (H) or K562 (K) cells with RAIDD antibody at 1:500 dilution.
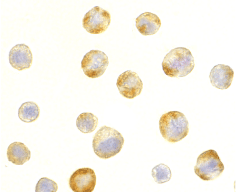
Below: Immunocytochemistry of RAIDD in HeLa cells with RAIDD antibody at 5 µg/ml.
Other Product Images
 Source : RAIDD antibody was raised against a peptide corresponding to amino acids 99 to 117 of human RAIDD .
Source : RAIDD antibody was raised against a peptide corresponding to amino acids 99 to 117 of human RAIDD .
Purification : Affinity chromatography purified via peptide column
Clonality and Clone : This is a polyclonal antibody.
Host : RAIDD antibody was raised in rabbit. Please use anti-rabbit secondary antibodies.
Immunogen : Human RAIDD (Intermediate Domain) Peptide (Cat. No. 1115P)
Application : RAIDD antibody can be used for detection of RAIDD by Western blot at 1:500 to 1:1000 dilution. A 22 kDa band should be detected.
Tested Application(s) : E, WB, ICC
Buffer : Antibody is supplied in PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide.
Blocking Peptide : Cat. No. 1115P - RAIDD Peptide
Long-Term Storage : RAIDD antibody can be stored at 4ºC, stable for one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures.
Positive Control
1. Cat. No. 1201 - HeLa Cell Lysate
2. Cat. No. 1204 - K562 Whole Cell Lysate
Species Reactivity :H
GI Number : 1785557
Accession Number : AAB42217
Short Description : (IN) Adapter Molecule
References
1. Duan H, Dixit VM. RAIDD is a new 'death' adaptor molecule. Nature 1997;385:86-89
2. Ahmad M, Srinivasula SM, Wang L, Talanian RV, Litwack G, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Alnemri ES. CRADD, a novel human apoptotic adaptor molecule for caspase-2, and FasL/tumor necrosis factor receptor-interacting protein RIP. Cancer Res 1997 57:615-619
3. Hofmann K, Bucher P, Tschopp J. The CARD domain: a new apoptotic signalling motif. Trends Biochem Sci 1997;22:155-156 (RD1299)
PUMA Monoclonal Antibody
Catalog# : PM-4529
Apoptosis is related to many diseases and development. The p53 tumor-suppressor protein induces apoptosis through transcriptional activation of several genes. A novel p53 inducible pro-apoptotic gene was identified recently and designated PUMA (for p53 upregulated modulator of apoptosis) and bbc3 (for Bcl-2 binding component 3) in human and mouse. PUMA/bbc3 is one of the pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 family members including Bax and Noxa, which are also transcriptional targets of p53. The PUMA gene encodes two BH3 domain-containing proteins termed PUMA-a and PUMA-b. PUMA proteins bind Bcl-2, localize to the mitochondria, and induce cytochrome c release and apoptosis in response to p53. PUMA may be a direct mediator of p53-induced apoptosis.
Additional Names : PUMA (10D4G7), p53 upregulated modulator of apoptosis, bbc3, Bcl-2 binding component 3
 Description
Description
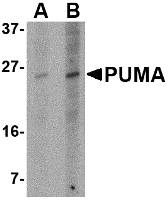
Left: Western blot analysis of PUMA expression in K562 cell lysate with PUMA antibody at (A) 2.5 and (B) 5 µg/ml.
Source : Mouse monoclonal PUMA antibody was raised against a recombinant protein corresponding to amino acids 76 – 170 of human PUMA-alpha.
Purification : Immunoaffinity chromotography purified IgG
Clonality and Clone : This is a monoclonal antibody. (Clone 10D4G7)
Host : PUMA monoclonal antibody was raised in mouse. Please use anti-rabbit secondary antibodies.
Immunogen : Recombinant protein corresponding to amino acids 76 – 170 of human PUMA-alpha.
Application : PUMA antibody can be used for detection of PUMA by Western blot at 2.5 to 5 µg/ml.
Tested Application(s) : E, WB
Buffer : Antibody is supplied in PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide.
Long-Term Storage : PUMA monoclonal antibody can be stored at 4ºC, stable for one year.
Positive Control
1. Cat. No. 1204 - K562 Whole Cell Lysate
2. Cat. No. 95-102 - PUMA Recombinant Protein
Species Reactivity :H, R
Short Description : p53 upregulated modulator of apoptosis
References
1. Nakano K, Vousden KH. PUMA, a novel proapoptotic gene, is induced by p53. Mol Cell. 2001; 7:683-94.
2. Yu J, Zhang L, Hwang PM, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B. PUMA induces the rapid apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells. Mol Cell. 2001; 7:673-82.
3. Han J, Flemington C, Houghton AB, Gu Z, Zambetti GP, Lutz RJ, Zhu L, Chittenden T. Expression of bbc3, a pro-apoptotic BH3-only gene, is regulated by diverse cell death and survival signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001; 98:11318-23.
PUMA Monoclonal Antibody
Catalog# : PM-4527
Apoptosis is related to many diseases and development. The p53 tumor-suppressor protein induces apoptosis through transcriptional activation of several genes. A novel p53 inducible pro-apoptotic gene was identified recently and designated PUMA (for p53 upregulated modulator of apoptosis) and bbc3 (for Bcl-2 binding component 3) in human and mouse. PUMA/bbc3 is one of the pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 family members including Bax and Noxa, which are also transcriptional targets of p53. The PUMA gene encodes two BH3 domain-containing proteins termed PUMA-a and PUMA-b. PUMA proteins bind Bcl-2, localize to the mitochondria, and induce cytochrome c release and apoptosis in response to p53. PUMA may be a direct mediator of p53-induced apoptosis.
Additional Names : PUMA (10C5G1), p53 upregulated modulator of apoptosis, bbc3, Bcl-2 binding component 3
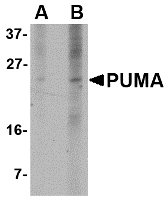 Description
Description
Western blot analysis of PUMA expression in K562 cell lysate with PUMA antibody at (A) 2.5 and (B) 5 µg/ml.
Source : Mouse monoclonal PUMA antibody was raised against a recombinant protein corresponding to amino acids 76 – 170 of human PUMA-alpha.
Purification : Immunoaffinity chromotography purified IgG
Clonality and Clone : This is a monoclonal antibody. (Clone 10C5G1)
Host : PUMA monoclonal antibody was raised in mouse. Please use anti-rabbit secondary antibodies.
Immunogen : Recombinant protein corresponding to amino acids 76 – 170 of human PUMA-alpha.
Application : PUMA antibody can be used for detection of PUMA by Western blot at 2.5 to 5 µg/ml.
Tested Application(s) : E, WB
Buffer : Antibody is supplied in PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide.
Long-Term Storage : PUMA monoclonal antibody can be stored at 4ºC, stable for one year.
Positive Control
1. Cat. No. 1204 - K562 Whole Cell Lysate
2. Cat. No. 95-102 - PUMA Recombinant Protein
Species Reactivity :H, R
Short Description : p53 upregulated modulator of apoptosis
References
1. Nakano K, Vousden KH. PUMA, a novel proapoptotic gene, is induced by p53. Mol Cell. 2001; 7:683-94.
2. Yu J, Zhang L, Hwang PM, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B. PUMA induces the rapid apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells. Mol Cell. 2001; 7:673-82.
3. Han J, Flemington C, Houghton AB, Gu Z, Zambetti GP, Lutz RJ, Zhu L, Chittenden T. Expression of bbc3, a pro-apoptotic BH3-only gene, is regulated by diverse cell death and survival signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001; 98:11318-23.
Custom DNA Synthesis
A wide variety of modifications can be incorporated directly during the synthesis or after synthesis. Certain modifications (notably Digoxigenin and some fluorescent dyes) are not available to be incorporated during synthesis and must be attached to the oligo after synthesis using NHS ester chemistry. NHS esters react with free primary amines and result in stable, covalent attachments. A primary amine is, therefore, added to the oligo during synthesis to permit reaction with the desired NHS ester. The post-synthetic chemical modifications made to an oligonucleotide by using NHS ester modification result in lower yields than direct incorporation of modifications during synthesis. Furthermore, all NHS ester modifications require HPLC purification. PAGE purification is not offered for NHS ester modifications as yields are further decreased and certain modifications can be damaged during PAGE purification.
Synthetic or naturally occurring peptides can be classified as linear or cyclic peptides. CP’s remain a very active area of synthetic interest, as more and more natural occurring CP’s are found in many flora and fauna, both terrestrial and aquatic. It has been found that CP’s often have increased metabolic stability, better receptor selectivity, controlled bioavailability and increased activity profiles. Also CP’s are metabolized more slowly due to their higher resistance to chemical degradation; on the other hand, due to their hydrophobicity they are excreted more readily than their corresponding linear counterparts. Many hormones, antibiotics, antimycotics and toxins in nature present themselves as CP’s. Many of these have been isolated, their structures resolved and produced by direct synthesis.
Cyclic Peptides
Cyclic peptides (CP’s) comprise those peptides where there is a bond formed, between two residues, whereby a closed loop is formed. They can be classified as homodetic ( where all bonds are true peptide bonds) and heterodetic (where there are both peptide bonds and other types of bonding, such as ester or cystine linkages) based upon the type of bonding found in them.
Cyclic Peptides Are Found in Marine Species
More recently there have been more CP’s found in plants, fungi, bacteria snails and a number of other marine organisms. They are useful in the study of receptor-ligand interaction due to their restricted conformation and decreased flexibility; therefore there is continuous interest in finding better synthetic routes and experimenting with modifications including but not limited to ring size, side chains and amino acid substitutions. Since the amounts found in their natural sources is often very minute, total synthetic routes remain the main/only option to obtain sufficient quantities for more in depth studies and analyses.
Head to Tail Cyclic Peptides
Cyclic peptides can be of the following topologies: head to tail, side chain to side chain, side chain to tail ( or head) and branched. Ring closure in side chain to side chain CP’s can be attained by disulfide or amide bond formation between sulfhydryl groups or the appropriate functionalities.
Custom Synthesis of Connotoxins
Of particular interest are connotoxins, small CP’s generally less than 12 amino acids, which have the unique characteristics of possessing 6 cysteines, which form 3 specific cystine bonds, conferring them their unique activities; some of these connotoxins have been found to have affinities 100X greater than morphine (phenathrene opiod receptor agonist) making them good candidates in the pain reducing research field, as they do not appear to induce addiction.
PUMA Monoclonal Antibody
Catalog# : PM-4525
Apoptosis is related to many diseases and development. The p53 tumor-suppressor protein induces apoptosis through transcriptional activation of several genes. A novel p53 inducible pro-apoptotic gene was identified recently and designated PUMA (for p53 upregulated modulator of apoptosis) and bbc3 (for Bcl-2 binding component 3) in human and mouse. PUMA/bbc3 is one of the pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 family members including Bax and Noxa, which are also transcriptional targets of p53. The PUMA gene encodes two BH3 domain-containing proteins termed PUMA-a and PUMA-b. PUMA proteins bind Bcl-2, localize to the mitochondria, and induce cytochrome c release and apoptosis in response to p53. PUMA may be a direct mediator of p53-induced apoptosis.
Additional Names : PUMA (2A9G5), p53 upregulated modulator of apoptosis, bbc3, Bcl-2 binding component 3
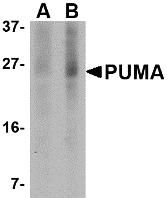 Description
Description
Left: Western blot analysis of PUMA expression in K562 cell lysate with PUMA antibody at (A) 2.5 and (B) 5 µg/ml.
Source : Mouse monoclonal PUMA antibody was raised against a recombinant protein corresponding to amino acids 76 – 170 of human PUMA-alpha.
Purification : Immunoaffinity chromotography purified IgG
Clonality and Clone : This is a monoclonal antibody. (Clone 2A9G5)
Host : PUMA monoclonal antibody was raised in mouse. Please use anti-rabbit secondary antibodies.
Immunogen : Recombinant protein corresponding to amino acids 76 – 170 of human PUMA-alpha.
Application : PUMA antibody can be used for detection of PUMA by Western blot at 2.5 to 5 µg/ml.
Tested Application(s) : E, WB
Buffer : Antibody is supplied in PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide.
Long-Term Storage : PUMA monoclonal antibody can be stored at 4ºC, stable for one year.
Positive Control
1. Cat. No. 1204 - K562 Whole Cell Lysate
2. Cat. No. 95-102 - PUMA Recombinant Protein
Species Reactivity :H, M, R
Short Description : p53 upregulated modulator of apoptosis
References
1. Nakano K, Vousden KH. PUMA, a novel proapoptotic gene, is induced by p53. Mol Cell. 2001; 7:683-94.
2. Yu J, Zhang L, Hwang PM, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B. PUMA induces the rapid apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells. Mol Cell. 2001; 7:673-82.
3. Han J, Flemington C, Houghton AB, Gu Z, Zambetti GP, Lutz RJ, Zhu L, Chittenden T. Expression of bbc3, a pro-apoptotic BH3-only gene, is regulated by diverse cell death and survival signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001; 98:11318-23.
PUMA Monoclonal Antibody
Catalog# : PM-4523
Apoptosis is related to many diseases and development. The p53 tumor-suppressor protein induces apoptosis through transcriptional activation of several genes. A novel p53 inducible pro-apoptotic gene was identified recently and designated PUMA (for p53 upregulated modulator of apoptosis) and bbc3 (for Bcl-2 binding component 3) in human and mouse. PUMA/bbc3 is one of the pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 family members including Bax and Noxa, which are also transcriptional targets of p53. The PUMA gene encodes two BH3 domain-containing proteins termed PUMA-a and PUMA-b. PUMA proteins bind Bcl-2, localize to the mitochondria, and induce cytochrome c release and apoptosis in response to p53. PUMA may be a direct mediator of p53-induced apoptosis.
Additional Names : PUMA (2A8F6), p53 upregulated modulator of apoptosis, bbc3, Bcl-2 binding component 3
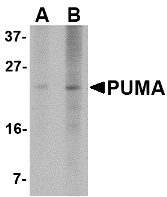 Description
Description
Left: Western blot analysis of PUMA expression in K562 cell lysate with PUMA antibody at (A) 2.5 and (B) 5 µg/ml.
Source : Mouse monoclonal PUMA antibody was raised against a recombinant protein corresponding to amino acids 76 – 170 of human PUMA-alpha.
Purification : Immunoaffinity chromotography purified IgG
Clonality and Clone : This is a monoclonal antibody. (Clone 2A8F6)
Host : PUMA monoclonal antibody was raised in mouse. Please use anti-rabbit secondary antibodies.
Immunogen : Recombinant protein corresponding to amino acids 76 – 170 of human PUMA-alpha.
Application : PUMA antibody can be used for detection of PUMA by Western blot at 2.5 to 5 µg/ml.
Tested Application(s) : E, WB
Buffer : Antibody is supplied in PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide.
Long-Term Storage : PUMA monoclonal antibody can be stored at 4ºC, stable for one year.
Positive Control
1. Cat. No. 1204 - K562 Whole Cell Lysate
2. Cat. No. 95-102 - PUMA Recombinant Protein
Species Reactivity :H, R
Short Description : p53 upregulated modulator of apoptosis
References
1. Nakano K, Vousden KH. PUMA, a novel proapoptotic gene, is induced by p53. Mol Cell. 2001; 7:683-94.
2. Yu J, Zhang L, Hwang PM, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B. PUMA induces the rapid apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells. Mol Cell. 2001; 7:673-82.
3. Han J, Flemington C, Houghton AB, Gu Z, Zambetti GP, Lutz RJ, Zhu L, Chittenden T.
 Description
Description























