Catalog# :5127
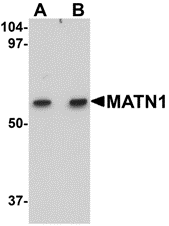
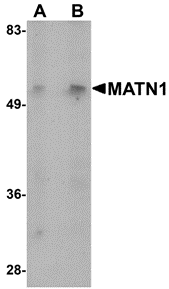
Matrilins (MATNs) are a family of non-collagenous extra-cellular matrix (ECM) proteins consisting of four known members that have been proposed to play key roles in modulating cellular phenotypes during chondrogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). MATN1 and MATN3 are expressed specifically in cartilage and are among the most up-regulated ECM proteins during chondrogenesis. MATN3 is composed of a single N-terminal von Willebrand Factor A (vWFA) domain followed by four epidermal growth factor (EGF) repeats and a coiled-coil domain whereas MATN1 is composed of two vWFA domains separated by one EGF-like domain. MATN1 or MATN3 may play a role in modulating chondrogenesis during the chondrocyte differentiation process. Mutations of this gene have been associated with variety of inherited chondrodysplasias. Recent studies show that aberrant expression and processing of MATN3 are hallmarks of conventional cartilaginous neoplasms.
Additional Names : MATN3 (CT), Matrilin 3,HOA, OS2, EDM5
 Description
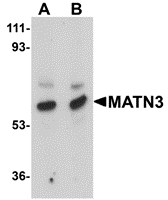
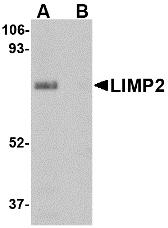
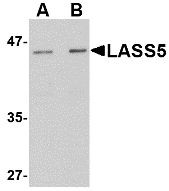
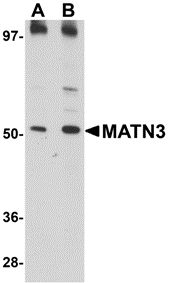
DescriptionLeft: Western blot analysis of MATN3 in 3T3 cell lysate with MATN3 antibody at (A) 1 and (B) 2 µg/ml.
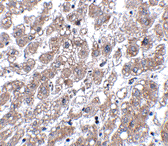
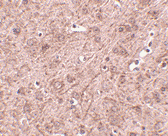
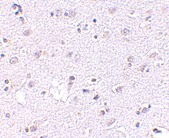
Below: Immunocytochemistry of MATN3 in 3T3 cells with MATN3 antibody at 5 μg/ml.
Other Product Images
 Source :MATN3 antibody was raised against a 13 amino acid peptide from near the carboxy terminus of human MATN3.
Source :MATN3 antibody was raised against a 13 amino acid peptide from near the carboxy terminus of human MATN3.Purification : Affinity chromatography purified via peptide column
Clonality and Clone : This is a polyclonal antibody.
Host : MATN3 antibody was raised in rabbit. Please use anti-rabbit secondary antibodies.
Application : MATN3 antibody can be used for detection of Matn3 by Western blot at 1 - 2 µg/ml.
Tested Application(s) : E, WB
Buffer : Antibody is supplied in PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide.
Blocking Peptide :Cat.No. 5127P - MATN3 Peptide
Long-Term Storage : MATN3 antibody can be stored at 4ºC, stable for one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures.
Positive Control :
1. Cat. No. 1282 - 3T3 (NIH) Cell Lysate
Species Reactivity : H, M, R
GI Number : 146218451
Accession Number : AAI39908
Short Description : (CT) Matrilin 3
References
1. Pei M, Luo J, and Chen Q. Enhancing and maintaining matrilins. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2008; 16:1110-7.
2. Frank S, Schulthess T, Landwehr R, et al. Characterization of the matrilin coiled-coil domains reveals seven novel isoforms. J. Biol. Chem. 2002; 277:19071-9.
3. Chen Q, Johnson DM, Haudenschild DR, et al. Progression and recapitulation of the chondrocyte differentiation program: cartilage matrix protein is a marker for cartilage maturation. Dev. Biol. 1995; 172:293–306.
4. Stokes DG, Liu G, Coimbra IB, et al. Assessment of the gene expression profile of differentiated and dedifferentiated human fetal chondrocytes by microarray analysis. Arthritis Rheum 2002; 46:404–19.