Catalog# : 3807
Apoptosis inhibitor of macrophages (AIM) is a member of the scavenger receptor cysteine-rich domain superfamily (SRCR-SF) initially identified as an inducible cell surface ligand of CD5. It was shown that AIM functions in the thymus as the inducer of resistance to apoptosis within CD4+/CD8+ thymocytes and as the supporter of the viability of these cells before thymic selection. AIM was also shown to support macrophage survival and enhance their phagocytic function. More recent experiments using recombinant AIM significantly inhibited apoptosis of NKT and T cells obtained from C. parvum-stimulated livers in vitro, suggesting that AIM functions to induce resistance to apoptosis in these cells and supports host defense against inflammation during infection.
Additional Names : AIM (NT), Apoptosis inhibitor of macrophages, API6, SP alpha, CD5L
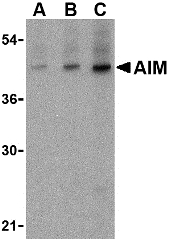 Description
DescriptionLeft: Western blot analysis of AIM in human lymph node tissue lysate with AIM antibody at (A) 1, (B) 2 and (C) 4 µg/ml. Below: Immunohistochemistry of AIM in human lymph node tissue with AIM antibody at 2 µg/ml.
Source : AIM antibody was raised against a 16 amino acid peptide near the amino terminus of human AIM.
Purification : Affinity chromatography purified via peptide column
Clonality and Clone : This is a polyclonal antibody.
Host : AIM antibody was raised in rabbit.
Tested Application(s) : E, WB, IHC
Buffer : Antibody is supplied in PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide.
Blocking Peptide : Cat.No. 3807P - AIM Peptide
Long-Term Storage : AIM antibody can be stored at 4ºC, stable for one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures.
Positive Control
- Cat. No. 1369 - Human Lymph Node Tissue Lysate
GI Number : 4102235
Accession Number : AAD01446
Short Description : (NT) apoptosis inhibitor of macrophages
References
- Miyazaki T, Hirokami Y, Matsuhashi N, et al. Increased susceptibility of thymocytes to apoptosis in mice lacking AIM, a novel murine macrophage-derived soluble factor belonging to the scavenger receptor cysteine-rich domain superfamily. J. Exp. Med. 1999; 189:413-22.
- Biancone L, Bowen MA, Lim A, et al. Identification of a novel inducible cell-surface ligand of CD5 on activated lymphocytes. J. Exp. Med. 1996; 184:811-9.
- Haruta I, Kato Y, Hashimoto E, et al. Association of AIM, a novel apoptosis inhibitory factor, with hepatitis via supporting macrophage survival and enhancing phagocytic function of macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 2001; 276:22910-4
- Kuwata K, Watanabe H, Jiang S-Y, et al. AIM inhibits apoptosis of T cells and NKT cells in Corynebacterium-induced granuloma formation in mice. Am. J. Path. 2003; 162:837-47.

No comments:
Post a Comment