Catalog# :PM-5201
CD4 is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily and is implicated as associative recognition element in MHC (Major Histocompatibility Complex) class II-restricted immune response. On T-lymphocytes, it defines the helper/inducer subset. The mature 55 kd CD4 protein consists of a 372 amino acid extracellular segment composed of four tandem immunoglobulin-like VJ regions. The CD4 molecule is a major receptor for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), binding directly to the envelope glycoprotein gp120 on HIV, with the co-receptors being CCR5 or CXCR4. It has been shown that the V-like domains are critical for binding with HIV envelope gp120.
Additional Names : CD4 (9H5A8), CD4 antigen, CD4 receptor
 Description
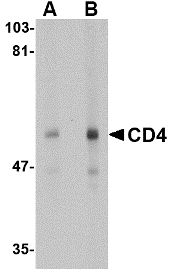
DescriptionLeft: Western blot analysis of CD4 in human thymus tissue lysate with CD4 antibody at (A) 0.5 and (B) 1 µg/ml.
Source :Mouse monoclonal CD4 antibody was raised against a 193 amino acid recombinant protein from near the amino terminus of human CD4.
Purification : Immunoaffinity chromotography purified IgG
Clonality and Clone : This is a monoclonal antibody. (Clone 9H5A8)
Host : CD4 monoclonal antibody was raised in mouse.
Please use anti-mouse secondary antibodies.
Immunogen : Mouse monoclonal CD4 antibody was raised against a 193 amino acid recombinant protein from near the
Application : CD4 antibody can be used for detection of CD4 by Western blot at 0.5 – 1 µg/ml.
Tested Application(s) : E, WB
Buffer : Antibody is supplied in PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide.
Blocking Peptide :
Long-Term Storage : CD4 monoclonal antibody can be stored at 4ºC, stable for one year.
Positive Control :
1. Cat. No. 1314 - Human Thymus Tissue Lysate
Species Reactivity : H, M, R
Short Description : CD4 antigen
References
1. Bowers K, Pitcher C, and Marsh M. CD4 : a co-receptor in the immune response and HIV infection. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1997; 29 :871-5.
2. Arthos J, Deen KC, Chaikin MA, et al. Identification of the residues in human CD4 critical for the binding of HIV. Cell 1989; 57:469-81.

No comments:
Post a Comment